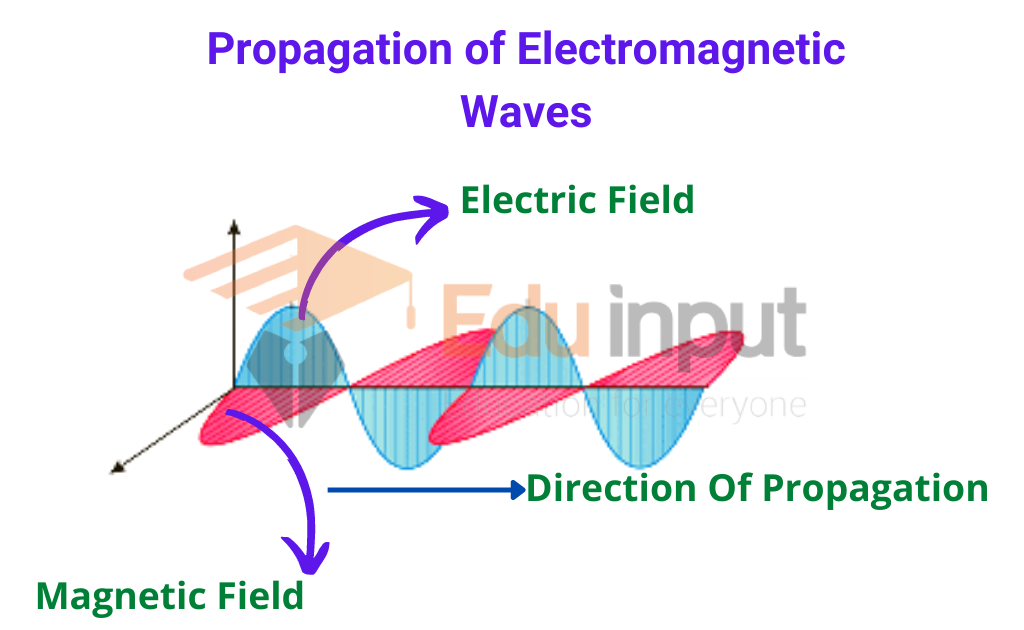
What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why . Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material. As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. And how does it interact with matter? What is an electromagnetic wave? Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields.
from eduinput.com
As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material. What is an electromagnetic wave? And how does it interact with matter? Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic.
Why is Wave a Transverse Wave?
What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. What is an electromagnetic wave? Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. And how does it interact with matter? Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material. Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate.
From www.sciencefacts.net
waves Definition, Propagation, and Types What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material. As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From www.vedantu.com
Waves Definition, Equation and Properties of What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. And how does it interact with matter? Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From www.env.go.jp
Types of Waves [MOE] What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Electromagnetic. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From www.vrogue.co
Wave Diagram vrogue.co What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. And how does it interact with. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From hebasoffar.blogspot.co.uk
Science online Examples and some technological applications of What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. What is an electromagnetic wave? And how does it interact with matter? Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From eduinput.com
10 Examples of Waves What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. And how does it interact with matter? What is an electromagnetic wave?. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From www.rfcafe.com
Understanding Wave Behavior RF Cafe What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. What is an electromagnetic wave? As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. And how does it interact with matter? Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics,. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From www.fity.club
Waves What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. And how does it interact with matter? Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From byjus.com
Why is light an wave? What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. What is an electromagnetic wave? And. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From www.alamy.com
wave hires stock photography and images Alamy What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material. And how does it interact with matter? As you might already. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From reversepcb.com
Definition of Waves Reversepcb What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. And how does it interact with matter? As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. What is an electromagnetic wave?. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From byjus.com
Arrange the following waves in the descending order of What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. Electromagnetic. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Waves Diagram What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material. What is an electromagnetic wave? Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. As. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From animalia-life.club
Wave Diagram What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From mungfali.com
What Are The Types Of Waves What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. And how does it interact with matter? What is an electromagnetic wave? As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields.. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From mungfali.com
Wave Diagram What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material. And how does it interact with matter? Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate. Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. As you might already. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From www.aakash.ac.in
Waves Definition, Characteristic, Equation and What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why And how does it interact with matter? Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. Learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic. What is an electromagnetic wave? Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.
From www.researchgate.net
2.A. spectrum. Two main characteristics of What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. As you might already know, a wave has a trough (lowest point) and a crest (highest. What is an electromagnetic wave? And how does it interact with matter? Electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through. What Are Electromagnetic Waves Why.